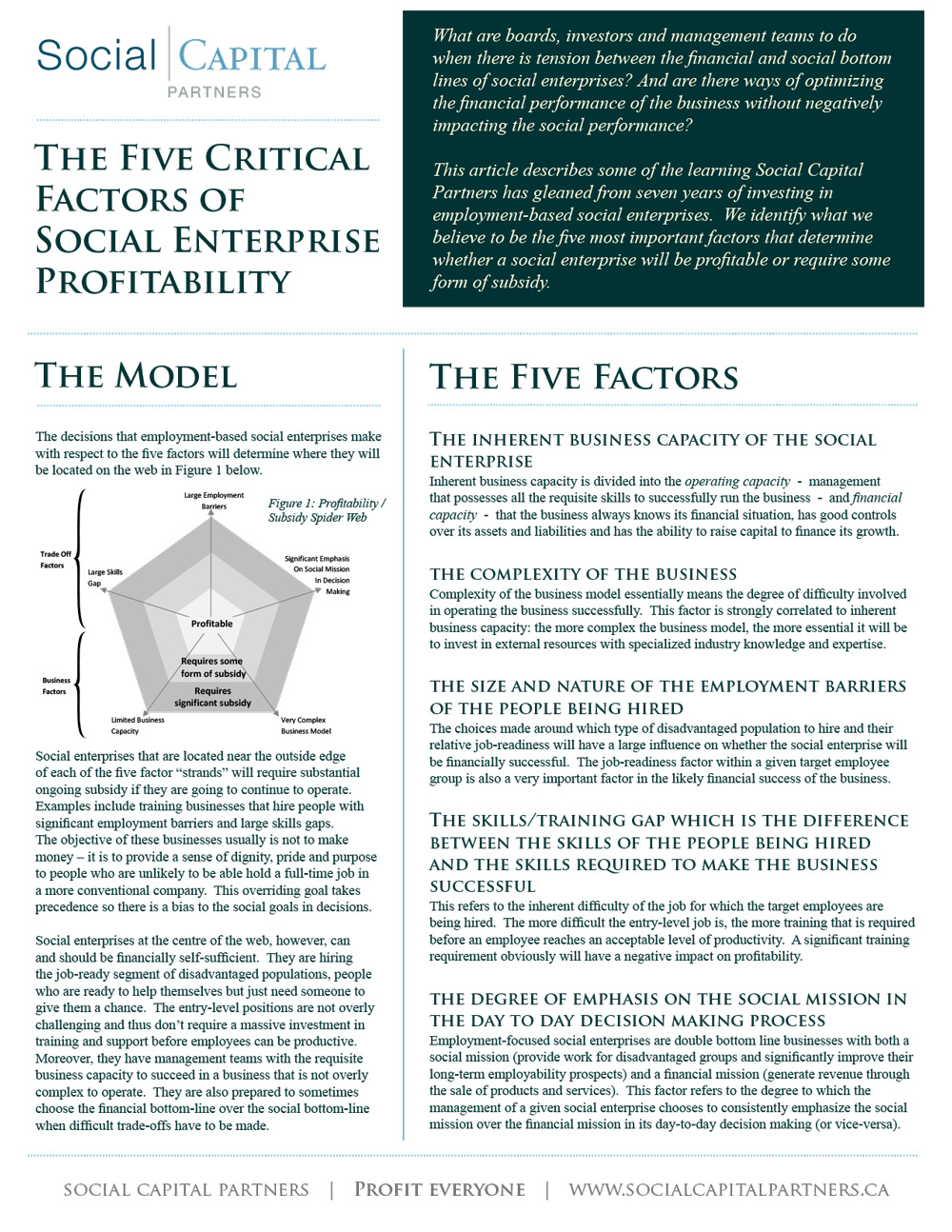
What are boards, investors and management teams to do when there is tension between the financial and social bottom lines of social enterprises? Social Capital Partners shares learnings gleaned from seven years of investing in employment-based social enterprises. We identify the five most important factors that determine whether a social enterprise will be profitable or require some form of subsidy.
Simply put, our advice is to do everything possible to choose businesses that are not overly complex to operate and to build management teams that have the inherent business capacity to operate them effectively.
Share with a friend
Related reading
Watch the video: Why would a company sell to its employees?
Canada is facing a $2-trillion business handoff. What if employees owned more of it? In this video, our Director of Policy Dan Skilleter explains why a company would sell to its own employees, how it happens and who stands to benefits. Spoiler alert: employee-owned companies are shown to be 8-12% more productive, share more wealth with their workers, keep businesses Canadian-owned and shore up the resilience of local communities and the broader economy.
How Canada can curb the serial acquisitions quietly reshaping our economy
In many cases, threats to the affordability of everyday goods and services are the byproduct of what competition experts call serial acquisitions—a pattern of larger firms buying up a series of smaller players to try and corner the market. As Michelle Arnold and Kiran Gill explain, a fair and competitive economy does not emerge by accident. The Competition Bureau's proposed Merger Enforcement Guidelines will play an important role in preventing bigger firms from creating unfair playing fields that hurt Canadian small businesses, workers and consumers. The next step for the bureau should be aggressive enforcement of the new guidelines.
From Guidelines to Action: Feedback on the Proposed Merger Enforcement Guidelines
The Competition Bureau's proposed Merger Enforcement Guidelines represent meaningful progress against trends towards corporate consolidation in Canada. In our formal feedback submission to the bureau, Social Capital Partners outlines that we strongly support the new guidelines. However, we believe that the operationalization of these guidelines will be the real test of their impact. Guidance documents shape expectations, but enforcement outcomes shape behaviour. Serial acquirers are sophisticated actors who model regulatory risk into their strategies. To succeed, the bureau must demonstrate visible capacity to track, analyze and challenge roll-up patterns that are driving up prices and sacrificing quality and service in key sectors.